Category: fertilizer making line investment
How to make small scale npk fertilizer
Creating NPK fertilizer on a small scale can be an enriching endeavor for home gardeners, small farms, or even start-up fertilizer producers. NPK stands for Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), the three primary nutrients required for healthy plant growth. Here is a comprehensive guide on how to make small-scale NPK fertilizer.
Understanding NPK Ratios
Before diving into production, it’s crucial to comprehend the NPK ratio, which reflects the proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the fertilizer. The specific needs of the plants being grown will dictate the ideal NPK ratio. A balanced 10-10-10 ratio is a common general-purpose fertilizer, but depending on the crop’s requirements, these ratios can vary.
Sourcing Raw Materials
Nitrogen Sources: For small-scale production, nitrogen can be sourced from blood meal, fish meal, or composted manure. Synthetic options include urea or ammonium sulfate.
Phosphorus Sources: Bone meal is a natural source of phosphorus. Alternatively, rock phosphate can be used if it is ground into a fine powder.
Potassium Sources: Wood ash is a natural source of potassium. Potassium sulfate or potassium chloride can also be used for a more concentrated source.
Equipment and Space
Basic Equipment
- Weighing scales for accurate measurement of ingredients
- Mixing tools such as a shovel or a mechanical mixer
- Protective gear like gloves and masks to prevent inhalation of dust
- Storage containers for both raw materials and the final product
Space Requirements
The space needed for small-scale production can be as simple as a well-ventilated shed or garage. Ensure the space is dry to prevent the fertilizer from clumping and that it is safe from contamination.
Production Process
Step 1: Measuring Ingredients
Using your weighing scales, measure out the raw materials according to the desired NPK ratio. Precision is essential here as it ensures the effectiveness of the final product.
Step 2: Grinding and Mixing
If the raw materials are not already in powdered form, they will need to be ground. Once powdered, mix the ingredients thoroughly to create a homogenous blend. A mechanical mixer can ensure a uniform mix, which is crucial for the fertilizer’s efficacy.
Step 3: Granulation (Optional)
For easier application, the mixed fertilizer can be granulated. Small-scale granulation can be done manually by creating small pellets and drying them, or with the use of a granulation machine. Compaction equipment is suitable for making small scale npk fertilizer.
Step 4: Curing and Drying
The mixture should be left to cure, which can take anywhere from several days to weeks. During this time, the chemical reactions between the components will occur. Following curing, the mixture should be completely dried to prevent mold or caking.
Step 5: Packaging and Storage
Once dry, the fertilizer can be packaged in airtight containers or bags. Label the packages with the NPK ratio and any instructions for use. Store the fertilizer in a cool, dry place until it’s ready to be used.
Safety Considerations
- Always wear protective gear to prevent skin irritation or inhalation of dust.
- Store raw materials and the final product safely to prevent contamination or accidental ingestion by children or pets.
- Ensure good ventilation when mixing and packaging the fertilizer.
Application Guidelines
To use the NPK fertilizer, follow the general rule of thumb of applying it every two to four months, depending on the crop’s needs. However, it’s essential to conduct soil tests to avoid over-fertilization, which can be harmful to plants and the environment.
Conclusion
Making small-scale NPK fertilizer can be a cost-effective and rewarding process, ensuring that the right balance of nutrients is available for plants. With careful planning, accurate measurements, and proper safety precautions, gardeners and small-scale farmers can produce their own high-quality fertilizer to foster bountiful growth and yields. And if you are interested in setting up a npk fertilizer plant, we can provude you with the best solution.
How to make compound phosphatic fertilizer
Compound phosphatic fertilizers are fertilizers that combine phosphate with other nutrients such as nitrogen and potassium to provide a balanced nutrient supply for crops. The manufacturing process for these fertilizers can be complex and requires careful planning and execution. Below is a comprehensive guide on the production of compound phosphatic fertilizer.
Understanding Compound Phosphatic Fertilizer
Composition and Benefits
Compound phosphatic fertilizers are tailored to meet the specific needs of crops by providing a balanced nutrient mix. Phosphate is crucial for root development and the maturation of crops, while the other nutrients support various physiological functions.
Raw Material Acquisition and Preparation
Sourcing Essential Components
The production of compound phosphatic fertilizer begins with sourcing raw materials. The primary ingredients are phosphate rock, ammonia, and potash. Depending on the target nutrient ratios, additional materials like urea or ammonium nitrate might be required.
Pre-Treatment of Phosphate Rock
Phosphate rock must be converted into a more soluble form to be accessible to plants. This is typically achieved through the production of phosphoric acid using the wet process, in which the phosphate rock is reacted with sulfuric acid.
Production Processes
Granulation Techniques
The production of compound phosphatic fertilizers often involves granulation, which can be done using different techniques such as rotary drum granulation, pan granulation, or extrusion granulator machinery. The choice of the method depends on the properties of the raw materials and the desired characteristics of the final product.
Mixing and Blending
The raw materials are accurately measured and thoroughly mixed to ensure a uniform distribution of nutrients. This is often carried out in a mixer or blender, where solid ingredients are combined before the granulation process.
Manufacturing Compound Phosphatic Fertilizer
The Granulation Process
During the granulation process, the mixed raw materials are transformed into granules. The materials may be bound together using a binding agent if necessary. The granules are then dried, cooled, and screened to produce a uniform size.
Adding Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients
Secondary nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, as well as micronutrients such as iron, manganese, zinc, copper, and boron, can be added either before or after granulation to enhance the fertilizer’s nutritive value.
Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring Product Quality
It is crucial to monitor the granulation process and perform regular quality control tests. The granule size, nutrient content, moisture levels, and strength of the granules are critical parameters that need to be checked to ensure a high-quality product.
Laboratory Analysis
Samples of the fertilizer are taken to a laboratory for analysis. This ensures that the product meets the specified nutrient content and is free from contaminants. Laboratory testing can also help optimize the manufacturing process by identifying areas for improvement.
Packaging and Storage
Appropriate Packaging Solutions
Once the compound phosphatic fertilizer has passed all quality control tests, it is packaged in suitable bags or containers that protect it from moisture and other environmental factors. The packaging is usually labeled with information regarding the nutrient content and application instructions.
Storage Considerations
Proper storage of compound phosphatic fertilizers is essential to maintain their efficacy. They should be stored in a cool, dry place to prevent caking and degradation. Bulk storage facilities should be designed to minimize contamination and facilitate easy handling.
Environmental and Safety Precautions
Handling and Safety Measures
Throughout the production process, it is essential to adhere to safety guidelines to prevent accidents and minimize exposure to dust, fumes, and chemicals. Workers should be equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Environmental Impact Mitigation
The production of compound phosphatic fertilizers should be carried out with environmental conservation in mind. This includes managing emissions, responsibly handling waste, and ensuring that effluents meet environmental standards.
Conclusion
The production of compound phosphatic fertilizer is a detailed process that requires careful selection of raw materials, precise blending, and controlled granulation. By following stringent quality control measures and adhering to environmental and safety regulations, manufacturers can produce effective and sustainable fertilizers that optimize crop growth and protect the health of the soil and the surrounding environment.
How Much Does It Cost To Build a Fertilizer Factory
The cost of building a fertilizer factory can vary significantly based on several factors, including the scale of the facility, the technology used, location, and regulatory requirements. Fertilizer production facilities can range from small-scale operations to large industrial complexes.
In general, the investment of fertilizer making can be broadly categorized into the following components:
Plant Size and Capacity
Larger fertilizer production plants with higher production capacities typically require more investment. The scale of the facility will influence the overall cost.
Technology and Equipment
The choice of technology and equipment for will impact fertilizer production costs. Advanced and efficient technologies may require a higher initial investment but could result in cost savings over time.
Raw Materials
The cost of raw materials, such as the primary ingredients used in fertilizer production (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Produced fertilizer type
Generally, the cost of organic fertilizer production is higher than NPK fertilizer plant investment. Because organic fertilizer need more equipment.
Labor Costs
Labor costs for construction, operation, and maintenance will contribute to the overall expenses.
Infrastructure and Utilities
Costs associated with infrastructure development, utilities (water, electricity, etc.), and transportation infrastructure can be significant.
Land Costs
The cost of acquiring or leasing land for the factory can be a significant factor, especially in urban or high-demand areas.
Engineering and Design
Costs associated with the engineering and design of the facility are part of the overall expenses. Here, some fertilizer equipment manufacture can offer you free system design. Click here to know more.
Contingency
It’s common to include a contingency budget to account for unforeseen circumstances or changes in project scope.
To get a more accurate estimate for your specific situation, you should consult with experts in fertilizer production, engineers, and financial analysts who can conduct a detailed feasibility study and provide cost estimates based on your project’s specific requirements. You can visit https://www.fertilizerbusinessplan.com/fertilizer-plant-cost/ for reference.

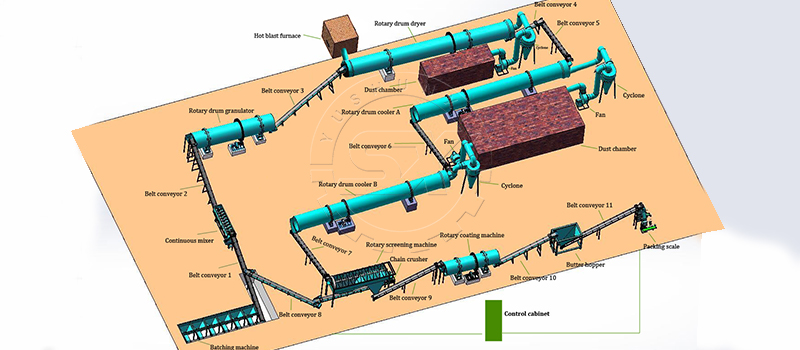
What machines can make phosphate fertilizer
April 7, 2024
fertilizer equipment, Fertilizer Granulating Machine, fertilizer making line investment, fertilizer making machine, fertillizer production line, phosphate fertilizer making
Comments Off on What machines can make phosphate fertilizer
cs
The production of phosphate fertilizers is a complex process that involves several steps and the use of various machines to transform raw phosphate rock into a usable product for agriculture. The primary objective of this process is to increase the availability of phosphorus for plant uptake, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth. Below, we will discuss the different types of machines that are instrumental in the production of phosphate fertilizers.
Mining Equipment: Extracting Phosphate Rock
Sub-surface Mining Machines
Phosphate rock is often extracted through sub-surface mining, which requires the use of specialized machines such as continuous miners and longwall mining equipment. These machines are designed to remove large quantities of overburden and phosphate-bearing ore from beneath the earth’s surface.
Draglines and Excavators
In other instances, open-pit mining techniques are employed, where draglines and hydraulic excavators are used to remove the overburden and extract the phosphate rock. These machines have large buckets that can remove significant amounts of earth in a single scoop, making them efficient for the task.
Milling Equipment: Processing Phosphate Rock
Crushers and Grinders
Once the phosphate rock is extracted, it must be processed to be converted into a form that can be used by plants. This begins with crushing and grinding the rock in crushers and grinders, which pulverize the raw phosphate to a smaller, more manageable size.
Ball Mills and Rod Mills
After crushing, the material is further processed in ball mills and rod mills, which are types of rotating drums that contain steel balls or rods. These mills work by tumbling the phosphate rock with the steel elements, thereby grinding it down into a fine powder, which is the consistency required for further processing.
Chemical Processing Machines: Producing Phosphoric Acid
Sulfuric Acid Reactors
One of the key steps in producing phosphate fertilizers is the creation of phosphoric acid. This is typically done by reacting the ground phosphate rock with sulfuric acid in large reactors. These reactors are designed to withstand the corrosive nature of sulfuric acid and allow for the controlled reaction between the acid and the phosphate rock.
Flash Coolers and Vacuum Filters
The resulting slurry from the reaction is then cooled and filtered. Flash coolers are used to rapidly cool down the hot slurry, while vacuum filters are employed to separate the phosphoric acid from the gypsum by-product.
Granulation Equipment: Forming Phosphate Fertilizers
Granulators and Drum Agglomerators
To convert the liquid phosphoric acid into solid fertilizer pellets, granulation machines are used. Granulators and drum agglomerators turn the mix of raw materials, including phosphoric acid and additives, into small, uniformly sized granules. The motion of these machines, along with added steam and binders, helps to form the round shape of the fertilizer pellets.
Dryers and Coolers
After granulation, the pellets are dried in rotary dryers to remove any remaining moisture. Subsequent cooling is necessary to strengthen the granules and prevent caking. Cooling is typically done in rotary coolers, which gently reduce the temperature of the fertilizer pellets.
Quality Control and Packaging Equipment
Screeners and Coaters
Before the final product can be packaged, it must be screened to sort the granules by size and ensure uniformity. Oversized or undersized granules are either crushed and re-granulated or discarded. Coating machines may be used to apply a fine layer of oil or other materials to enhance the product’s handling characteristics.
Packaging Machines The final step involves packaging the phosphate fertilizer into bags or bulk containers. Automated packaging machines fill and seal bags with precise amounts of fertilizer, ready for distribution and use on farms.
In conclusion, the production of phosphate fertilizers is a multi-faceted process that relies on a variety of machines, each designed to perform specific tasks from extracting phosphate rock to packaging the final product. The efficient operation of these machines is crucial to ensuring a steady supply of this important agricultural input.
how to make phosphate fertilizerphosphate fertilizer making machines